This study investigated the immediate effects of Galileo Mano Training (vibration dumbbell) on muscle power and muscle activation (EMG) in elite boxers (5x 1 min., 30Hz, 145° bent arms). One arm was trained the other was used as internal control. The side trained with Galileo could improve muscle power when lifting 5% of body mass by 13%. During Galileo Training muscle activation was increased by 110%...
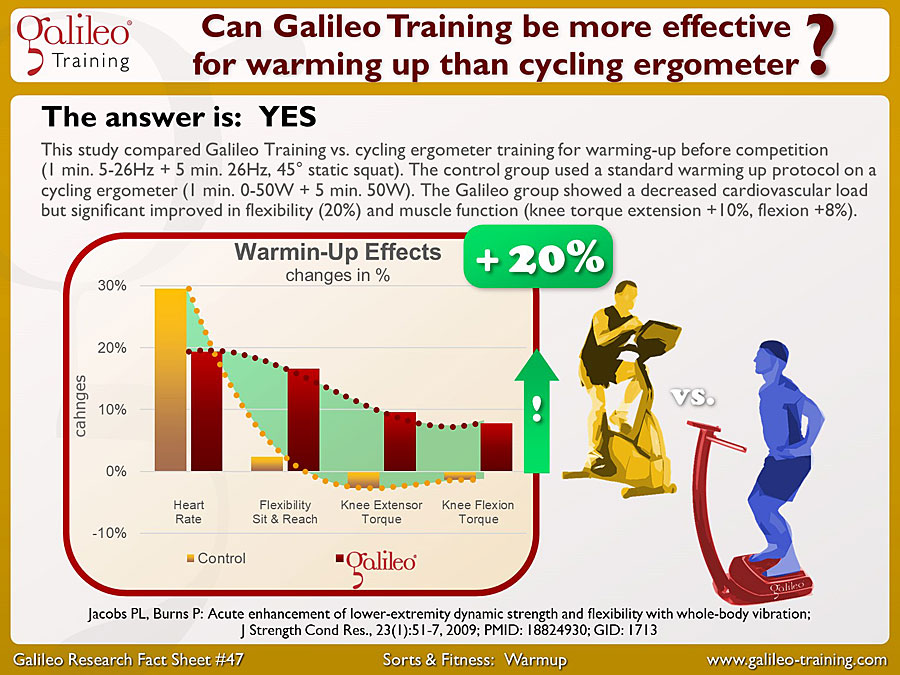
Galileo Research Facts No. 47: Can Galileo Training be more effective for warming up than cycling ergometer?
This study compared Galileo Training vs. cycling ergometer training for warming-up before competition (1 min. 5-26Hz + 5 min. 26Hz, 45° static squat). The control group used a standard warming up protocol on a cycling ergometer (1 min. 0-50W + 5 min. 50W). The Galileo group showed a decreased cardiovascular load but significant improved in flexibility (20%) and muscle function (knee torque extension +10%, flexion +8%)...
Galileo Research Facts No. 46: Can Galileo Training reduce Creatin Kinase after extensive endurance Training?
This study tested the effect of Galileo Training on Creatine Kinase (CK) concentration after exhaustive endurance training. Both groups trained treadmill + 4x400 (HIIT) + 3km Time-Trial. The Galileo Group trained at 12Hz (5x60 sec. slight squats, 5x30 sec. sitting with feet on Galileo). 24 h after the intensive endurance training Creatine Kinase levels where reduced by 20% in the Galileo group compared to control...
Galileo Research Facts No. 45: Can Galileo Training in artificial weightlessness prevent bone loss?
The first Galileo Space-Study examined its effects on muscle and bone mass in simulated weightlessness (55 days bedrest, 10 min., 5 days/week 12-26Hz). The control group did not have any training. While the control group showed massive loss of bone mass (over 15%) the Galileo Group could almost completely compensate this effect (in strict bed-rest over 55 days!) and even showed higher bone mass (+4%) after 1 year follow-up...
Galileo Research Facts No. 44: Can Galileo Training in artificial weightlessness prevent loss of muscle and muscle function?
The first Galileo Space-Study examined its effects on muscle and bone in simulated weightlessness (55 days bedrest, 10 min., 5 days/week 12-26Hz). The control group did not have any training. While the control group showed massive loss in muscle cross-section, the Galileo groups hardly lost any muscle and could even improve muscle function (max torque) by 12% (in strict bed-rest over 55 days without any other exercise!)...
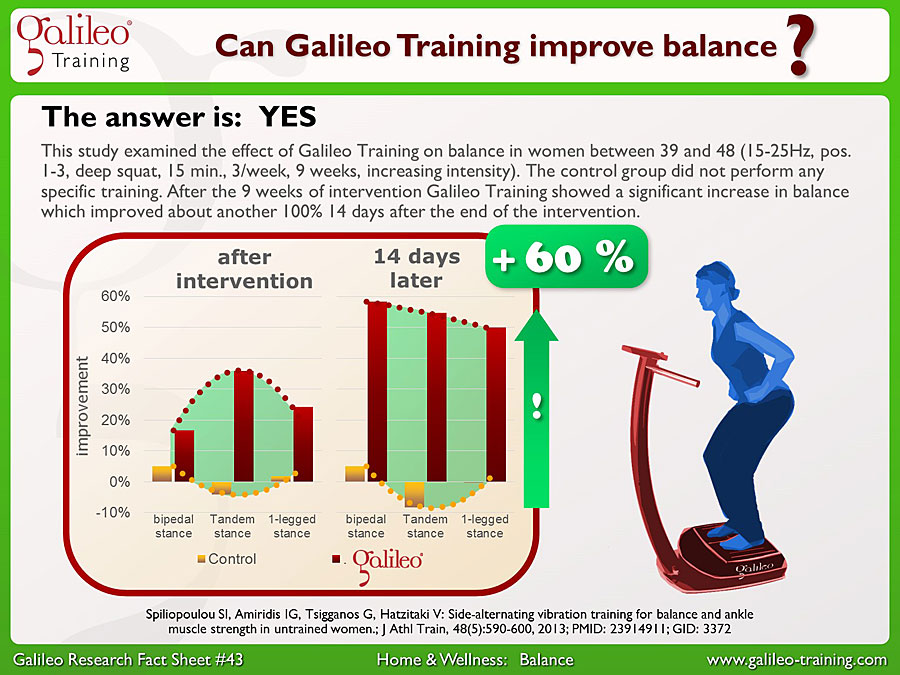
Galileo Research Facts No. 43: Can Galileo Training improve balance?
This study examined the effect of Galileo Training on balance in women between 39 and 48 (15-25Hz, pos. 1-3, deep squat, 15 min., 3/week, 9 weeks, increasing intensity). The control group did not perform any specific training. After the 9 weeks of intervention Galileo Training showed a significant increase in balance which improved about another 100% 14 days after the end of the intervention...
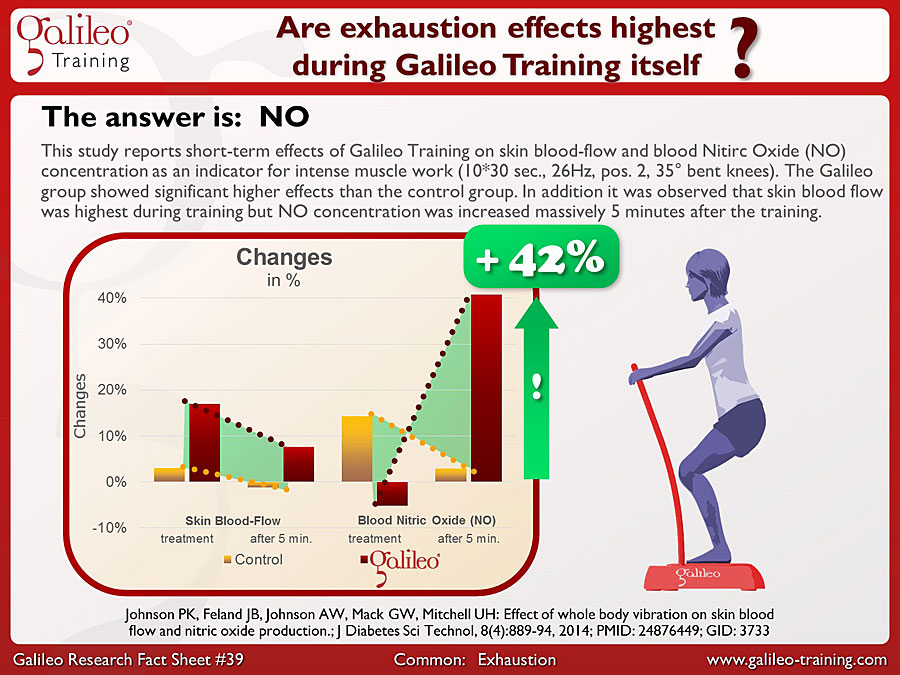
Galileo Research Facts No. 39: Are exhaustion effects highest during Galileo Training itself?
This study reports short-term effects of Galileo Training on skin blood-flow and blood Nitirc Oxide (NO) concentration as an indicator for intense muscle work (10*30 sec., 26Hz, pos. 2, 35° bent knees). The Galileo group showed significant higher effects than the control group. In addition it was observed that skin blood flow was highest during training but NO concentration was increased massively 5 minutes after the training...
Galileo Research Facts No. 38: Can 75 seconds of Galileo warm-up training increase flexibility, performance and balance?
The study reported the immediate effects of 75 seconds of a special Galileo Based warm-up training on flexibility, jumping performance and balance in Olympic rhythmic gymnasts (5*15 sec., 30Hz, pos. 2). The control group did the same 5 exercises without vibration. The Galileo group showed immediately and 15 min. after the exercises improvements of up to 15% while the control groups showed no significant improvements...
Galileo Research Facts No. 35: Can Galileo Training increase jumping performance after only 10 days?
The first Whole Body Vibration Training study ever, done with Galileo in 1998. It shows the effects of Galileo Training on Jumping performance in active handball and water polo players (26Hz, pos. 5, 5*2 min., 10 days, 1) forefoot 2) 45° squat 3) 90°squat 4/5) 90°squat one legged). Both groups performed additional 20 min. warmup and 5 min. jump training. Only the Galileo Training group showed jump improvements of up to 12%...
Galileo Research Facts No. 33: Can one set Galileo Training + Blood Flow Restriction activate muscle Satellite cells?
This study reports short-term effects of Galileo Training on skin blood-flow and blood Nitirc Oxide (NO) concentration as an indicator for intense muscle work (10*30 sec., 26Hz, pos. 2, 35° bent knees). The Galileo group showed significant higher effects than the control group. In addition it was observed that skin blood flow was highest during training but NO concentration was increased massively 5 minutes after the training...