Galileo® in space research
Galileo® to prevent muscle and bone loss in space
our focus
Focus of our space-research projects are counter measures – especially novel training concepts – acting against the negative effects of longer space missions on neurology, muscle an bone.
But our product spectrum not only cover unique training devices, but also the measurement technology needed to objectively and precisely document these changes .
Effects of microgravity
As a consequence of the lack of usage of the muscles of the legs, Astronauts show a loss of muscles and bone. Therefore, prolongued space flights typically result in a local Osteopeneia preliminary stage of Osteoprosis, even though they train 1 to 2 hours a day.
INNOVATIVE Training-Systems
To compensate these negative effects space research seeks for innovative training methods - co called so called counter measures, which can be used in space. For this research we did develop several such novel systems in different research projects for the European Space Agency (ESA) as well as the German Space Agency (DLR). Several studies showed that the application of Galileo Space is not only effective but is also very little time-consuming.
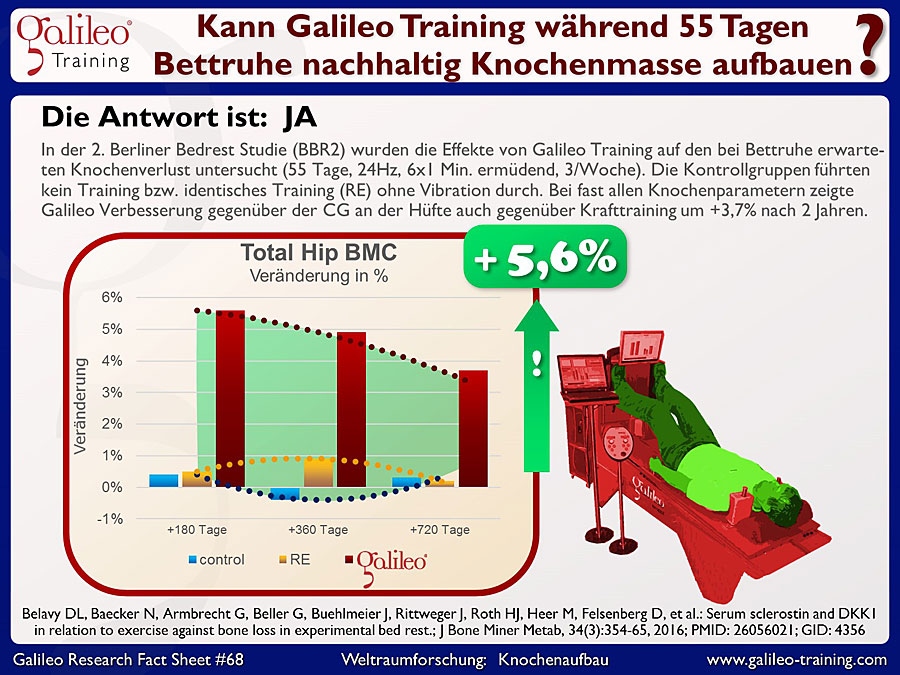
BED-REST STUDIES
The typical type of studies to validate the effects of such counter measure systems are so-called bed-rest studies, where young, healthy individual spend two months completely in bed - without standing up for anything. This stimulates effects similar to those in space caused by disuse especially of the muscles of the legs. As a consequence the untrained loose in those 2 months about 2-4% of bone mass at the lower leg (locally even up to 20%) and about 20-30% of muscle mass. While muscle mass can be re-gained by training within a few weeks, bone needs about 1 to 2 years - even for these joung and healthy individuals.
WHY IS THIS RESEARCH SO IMPORTANT?
Interestingly, these effects due to the micro-gravity in space are very similar to Osteoporosis. This is because genetic preposition as well as lack of usage result in similar effects on bone. This is why space research gives important input for the fields of Osteoporosis and Sarcopenia - especially since traditional Osteoporosis is a combination of preposition and decreased (or inadequate) physical activity. While there's not much to be changed for the first, the second can be influenced significantly - especially when using Galileo®.
Galileo® Space
Galileo® is the vibration training device, which is used frequently in space research.


Do you have questions about our products or would you like to purchase a product?
Let our experts advise you. Just contact us.
Our cooperation partners world-wide
MUSCLE- AND BONE RESEARCH IN SPACE MEDICINE
Find out about our customers of training systems and measurement devices.
DLR, Cologn
https://www.dlr.de
Institute of Aerospace Medicine
Traininf systems to prevent loss of bone mass and neuro-muscular function during prolongued space flights.
https://www.dlr.de/me/desktopdefault.aspx/tabid-1752/
- Novel Counter-Measure Systems
- Bedrest-Studies
Parabolic Flight Campaigns:
- 2006 – Galileo Space: Feasability study about vibration training in mciro gravity
- 2009 – Galileo Space: Neurological effects of vibration training in micro-gravity
- 2010 – Galileo Space: COnsequences on balance
:envihab
https://www.dlr.de/envihab/
- Galileo Space on teh short-arm centrifuge at the DLR :envihab
Novel training devices to prevent loss of bone mass and muscle function during prologued space flights.
- ICS – Integrated Counter Measure System (2008)
- NEX4EX – Novel Exercise Hardware for Exploration (2019)
Computer-tomography for application in space
- XRAI – X-Ray Based Analytical Imaging Device (1013)
Bed-Rest Studies
- LTBR – Toulouse Bedrest Study (2003)
- BBR1 – Berlin Bedrest Study (2003)
- BBR2 – Berlin Bedrest Study 2 (2007)
- Toulouse Bedrest Study (2012)
- Cologne Bedrest Study (2019)
Long-term studies
- Mars500 – Simulated 520 day flight to Mars (2010)
Short-arm Centrifuges
- DLR :envihab (2015)
- IJS (Institut Jožef Stefan) (2020)
IJS – Institut Jozef Stefan
https://www.ijs.si/ijsw/IJS
Novel training devices to prevent loss of bone mass and muscle function during prologued space flights.
- Short-arm centrifuge
- Galileo Space Centrifuge
ZMK – Centre for Muscle and Bone Research
Prof. Dieter Felsenberg
https://zmk.charite.de/
Bedrest-Studies about novel training devices to prevent loss of bone-mass and muscle function during prologued space flights.
- BBR – Berliner Bedrest Study (2003)
- DLR Parabolic Flight Campaign – Demonstrator Galileo Space: Vibration training in micro gravity (2006)
- BBR2 – Berliner Bedrest Study 2 (2007)
- Mars 500 – 520 day simulation of flight to Mars (2010)
- Concordia – Muscle- and bone assessments at the european Concordia Antartica base (2015-22)
Chair of Training and Movement Science
Prof. Markus Gruber
https://www.sportwissenschaft.uni-konstanz.de/
Bedrest-Studies about novel training devices to prevent loss of bone-mass and muscle function during prologued space flights.
- ICS – Integrated Counter Measure System (2008)
- DLR Parabolic Flight Campaign – Galileo Space: Consequences on balance (2010)
- Cologne Bedrest Study (2019)
- NEX4EX – Novel Exercise Hardware for Exploration (2019)
Department of Sport and Sport Science
Prof. Albert Gollhofer
https://www.sport.uni-freiburg.de/de
Studies abut novel training systems for prevention of loss ob bone mass and neuro-muscular function during space flights.
- ICS – Integrated Counter Measure-System (2008)
- DLR parabolic flight champagne – Galileo Space: Neurological effect of vibration training in micro-gravity (2009)
Our projects in space research
PROJECTS SINCE 2001 AND THE INVOLVED PRODUCT GROUPS
- 2001: Toulouse Bedrest Study (LTBR) (Stratec pQCT, Leonardo Mechanography)
- 2003: Berlin Bedrest Study (BBR) (Stratec pQCT, Leonardo Mechanography, Galileo Space)
- 2006: DLR Parabolic Flight Campaign (Galileo Space)
- 2007: Berlin Bedrest Study 2 (BBR2) (Stratec pQCT, Leonardo Mechanography, Galileo Space Sensor)
- 2008: DLR Bedrest Study (short-term) (Galileo Space)
- 2008: Integrated Counter Measure (ICS) (Sledge Jump System, Galileo Space Sensor)
- 2009: DLR Parabolic Flight Campaign (Galileo Space)
- 2010: DLR Parabolic Flight Campaign (Galileo Space)
- 2010: Mars 500 Mission (Stratec pQCT, Leonardo Mechanography, Galileo Advanced)
- 2012: Toulouse Bedrest Study (Galileo Space Sensor)
- 2013: pQCT-System for Space (XRAI) (Stratec pQCT)
- 2015: DLR :envihab Short Arm Centrifuge (Galileo Space Centrifuge)
- 2015: Concordia (Antartica) (Stratec pQCT, Leonardo Mechanography)
- 2017: DLR Bedrest Study SJS (Sledge Jump System)
- 2019: ICS upgrade: NEX4EX (Sledge Jump System, Galileo Space Sensor)
- 2020: IJS Short Arm Centrifuge (Galileo Space Centrifuge)
- 2023: IJS Additional Galileo Space Systems (Galileo Space Centrifuge)
Our brands
Galileo® Training, Galileo® Therapy, xelerate®.you,
Leonardo Mechanograph® & PQCT