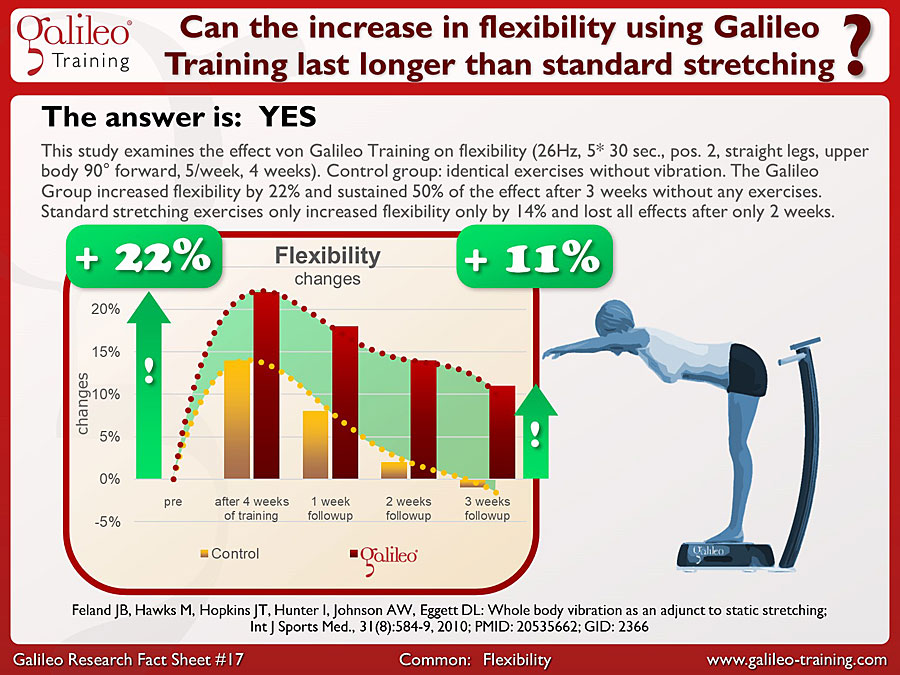
This study examines the effect von Galileo Training on flexibility (26Hz, 5* 30 sec., pos. 2, straight legs, upper body 90° forward, 5/week, 4 weeks). Control group: identical exercises without vibration. The Galileo Group increased flexibility by 22% and sustained 50% of the effect after 3 weeks without any exercises. Standard stretching exercises only increased flexibility only by 14% and lost all effects after only 2 weeks...
Galileo Research Facts No. 16: Can Galileo Training even at high frequencies improve flexibility?
This study tested the short-term effect of Galileo Training on flexibility (26 Hz, 6 minutes, slightly bent knees, 170°). The control group used a cycling ergometer for 6 minutes at moderate 50W). As a result the flexibility measured by sit & reach test improved by 17%, torque in knee extension by 10% and torque in knee flexion by 8%. The control group did not show any significant changes...
Galileo Research Facts No. 12: Can Galileo Training increase endurance?
This study shows the effect of 16 Galileo Sessions (8 weeks, 30Hz, start 60% body weight, plus Occlusion) fro a group of young women compared to identical resistance training without vibration. The Galileo group increased the resistance by 85%, endurance by 57%, peak power on the ergometer by 9% (Wingate Rest); The resistance control group did not show a significant positive effect...
Galileo Research Facts No. 11: Can endurance athletes also gain with Galileo Training?
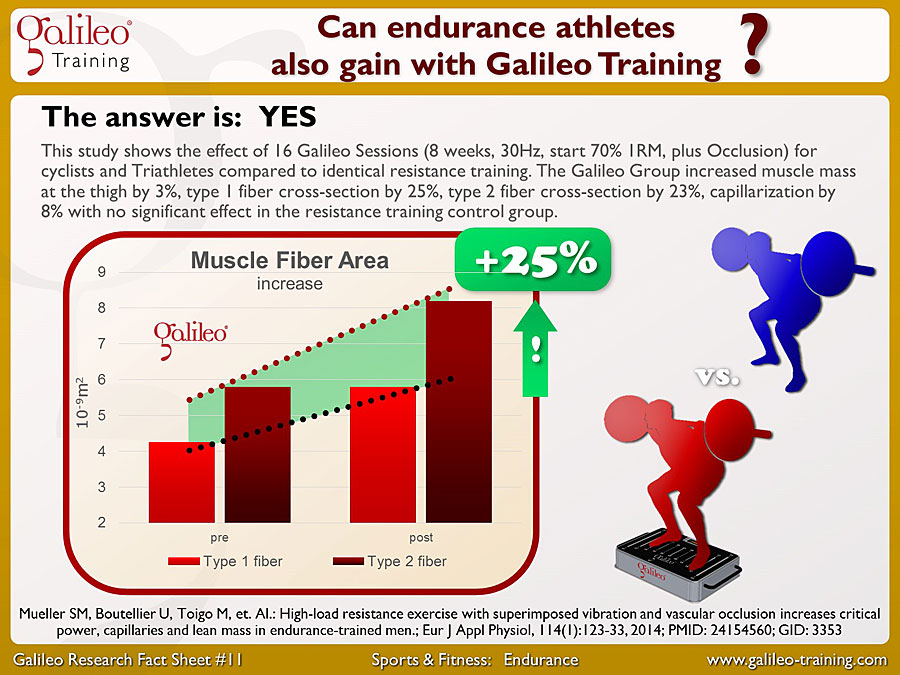
This study shows the effect of 16 Galileo Sessions (8 weeks, 30Hz, start 70% 1RM, plus Occlusion) for cyclists and Triathletes compared to identical resistance training. The Galileo Group increased muscle mass at the thigh by 3%, type 1 fiber cross-section by 25%, type 2 fiber cross-section by 23%, capillarization by 8% with no significant effect in the resistance training control group...
Galileo Research Facts No. 10: Can Galileo Training increase jumping height in older individuals?
This study investigated the effect of Galileo Training on jumping height in 45 to 63 year old individuals. They performed 12 training session at 30 Hz within 6 weeks. As a result jumping height increased by almost 20% while there was no significant change in the control group. The authors therefore suggested Galileo Training as an alternative to standard strength training methods...
Galileo Research Facts No. 8: Can Galileo Training activate muscles of the back?
This study examines the activation (EMG) of different muscles of the back during Galileo Training at different knee angles. It shows that Galileo activates the muscles of the back up to 18% higher than just standing in the same position. Muscles of the back were activated up to 27% of the maximum voluntary contraction (MVC). Galileo Training therefore significantly increases muscle activation of the back...
Galileo Research Facts No. 7: Does Galileo Training cause high joint forces?
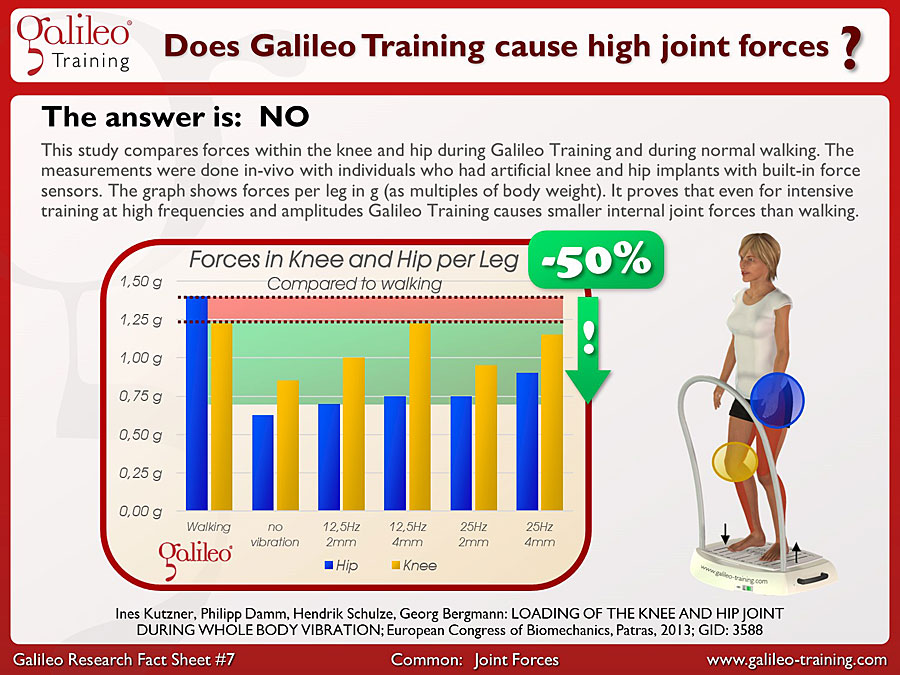
This study compares forces within the knee and hip during Galileo Training and during normal walking. The measurements were done in-vivo with individuals who had artificial knee and hip implants with built-in force sensors. The graph shows forces per leg in g (as multiples of body weight). It proves that even for intensive training at high frequencies and amplitudes Galileo Training causes smaller internal joint forces than walking.
Galileo Research Fact Sheet No. 6: Are joint forces during Galileo Training higher than during vertical vibration?
This study compares muscle activation of the legs (EMG) of Galileo Training compared to vertical vibration (30Hz and 2mm amplitude). Compared to vertical vibration Galileo Training results in up to 150% higher additional activation of the muscle using identical amplitude and frequency (100% equivalent to standing)...
Galileo Research Facts No. 5: Can Galileo Training reduce Creatine Kinase (CK)?
Diese Studie untersucht den Einfluss von Galileo Training auf Muskelkater. Beide Gruppen trainierten exzentrische Quadrizeps Extension bei 120% 1RM. Die Galileo Gruppe trainierte anschließend 3 Min. mit Galileo bei 12Hz. Galileo Training halbierte den subjektiven Muskelkater und reduzierte die Creatin-Kinase-Werte (CK) um 40%...
Galileo Research Facts No. 4: Does muscle activation increase with knee angle and additional loads?
This study tested the activation (EMG) of the leg muscles at different training frequencies, knee angles and additional loads of 30% body mass. It showed that squats cause significantly higher muscle activation which can be further increased by using additional loads. This way muscle activation can be tripled (+210%)...