Our news at a glance
Here you will find a chronological overview of all news. Select one of the categories or search our news using the search function in the left-hand column.
17. September 2023
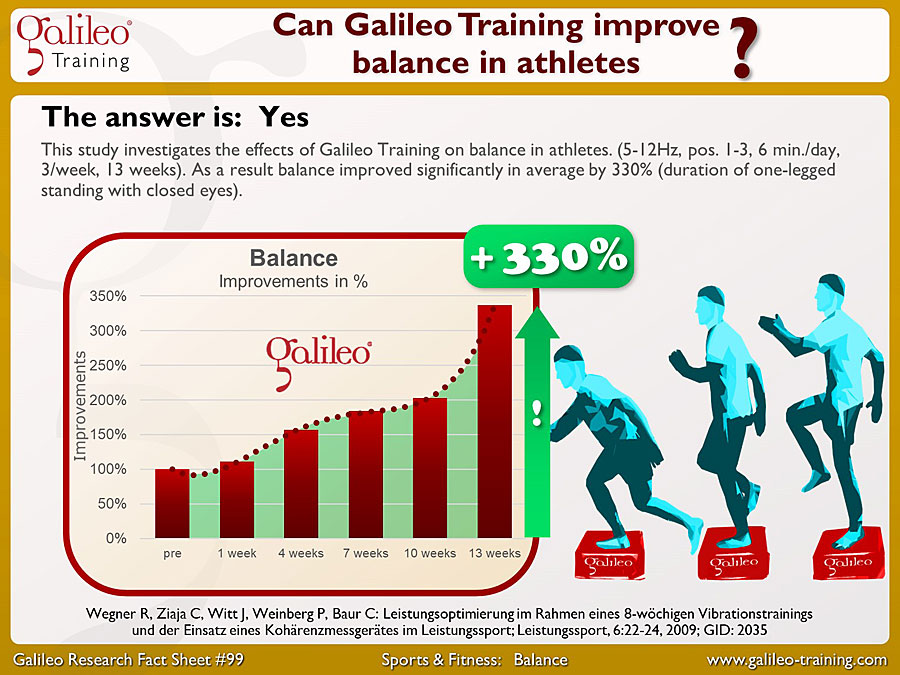
Galileo Research Facts No. 99: Can Galileo Training improve balance in athletes?
This study investigates the effects of Galileo Training on balance in athletes. (5-12Hz, pos. 1-3, 6 min./day, 3/week, 13 weeks). As a result balance improved significantly in average by 330% (duration of one-legged standing with closed eyes)...

17. September 2023
Galileo Research Facts No. 98: Can Galileo Therapy at work decrease subjective back pain?
This study documented the effects of workplace-based Galileo Therapy on subjective back pain in individuals with chronic lower-back pain (10-30Hz, slightly bent legs, pos. 1-3, 15 min., 2-3/weeks, 3 months). The control group received no therapy. While the control group slightly decreased the Galileo Therapy group improved by up to 4.5% and showed a tendency to decrease days of sick-leave per month...
17. September 2023
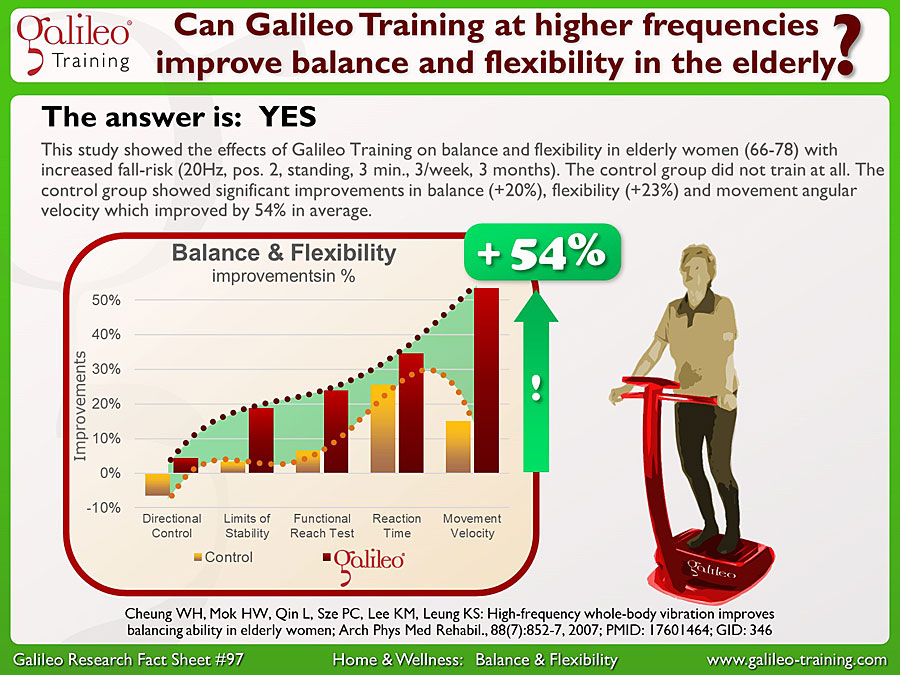
Galileo Research Facts No. 97: Can Galileo Training at higher frequencies improve balance and flexibility in the elderly?
This study showed the effects of Galileo Training on balance and flexibility in elderly women (66-78) with increased fall-risk (20Hz, pos. 2, standing, 3 min., 3/week, 3 months). The control group did not train at all. The control group showed significant improvements in balance (+20%), flexibility (+23%) and movement angular velocity which improved by 54% in average...

17. September 2023
Galileo Research Facts No. 96: Is muscle activity during Galileo Training related to different postures?
This study investigates the effects of different tilt-angles of the hip during Galileo Training on muscular activation (EMG) (10 sec., 0Hz/10HZ/20Hz, pos. 2, legs slightly flexed). The results show that muscular activation is strongly dependent on posture. The observed effects during Galileo Training depend on the tested muscle groups as well as frequency and can be as high as 2250%...

17. September 2023
Galileo Research Facts No. 95: Does muscular activation with Galileo Training increase with increasing frequency?
This study investigates the effects of different frequencies during Galileo Training on muscular activation (EMG) (10 sec., 0Hz/10HZ/20Hz, pos. 2, legs slightly flexed). The results show that increasing frequencies cause increasing muscular activation. The observed effects during Galileo Training depend on the tested muscle groups as well as posture and can be as high as 2250%...

17. September 2023
Galileo Research Facts No. 94: Can Galileo Therapy improve the disability status of MS patients?
This study investigated the effects of 8 weeks of Galileo Therapy on different disease related scores (PDDS, MSCF) in MS (Multiple Sclerosis) patients (20Hz, pos. 1.5, 5*1 min., 3/week, 8 weeks, 20° bent legs). The results show not only improvements in PDDS and PSAT-3 by up to 18% but also an increase in HSFC (MS Functional Composite: walking distance, hand function, calculation test) in average by 0.36SD...

17. September 2023
Galileo Research Facts No. 93: Can 5*10 min./week Galileo Training prevent loss of muscle function during 55 days bedrest?
During the 1st Berlin Bedrest Study (BBR) individuals had to stay in bed for 55 days completely. The control group did no training at all, the Galileo group received 10 Min., 5 days/week 12-26Hz of intense Galileo Training while in bed. The Galileo group could prevent loss of muscle function almost completely while the control group lost muscle function by up to 28%...

17. September 2023
Galileo Research Facts No. 92: Can frequent Galileo Training improve the immune system?
During the 2nd Berlin Bedrest Study (BBR2) the participants had to stay in bed for 55 days. The control group received no intervention at all, the Galileo Training group did resistance exercise + vibration (24Hz, 6x1 min. to exhaustion, 3/week). The control group showed a decrease in immune system (increased inflammation markers decreased immune competence & function) while the Galileo group improved the immune system...

17. September 2023
Galileo Research Facts No. 91: Can Galileo Therapy decrease Creatine Kinase levels in Duchenne (DMD) patients?
This study shows the effect of Galileo Therapy on Creatine Kinase (CK) levels in Duchenne Patients (5-20Hz, 2*1 to 2*2 min., 3/week, 12 weeks). Over a period of 3 months the CK levels dropped essentially by 98% and increases again after the end of the therapy period. CK is believed to indicate the amount of muscle fiber damage due to extensive muscle activity and therefore should be kept low in Duchenne patients...

17. September 2023
Galileo Research Facts No. 90: Can Galileo Training decrease Creatine Kinase levels during bedrest?
During the 2nd Berlin Bedrest Study (BBR2) the participants had to stay in bed for 55 days. The control group did no training at all, the Galileo group did resistance training + vibration (24Hz, 6x1 min. to exhaustion, 3/week). The Galileo group decreased CK levels to the same values ad the passive control group but received even better training results than the resistance training group which showed the highest CK levels in bedrest...